뮤트 개발일지
AIFFEL 아이펠 9일차 본문
붓꽃 분류 문제
사이킷런(scikit-learn): 머신러닝에서 가장 많이 쓰이는 라이브러리 중 하나. 사이킷런에 내장된 데이터로 붓꽃 데이터가 있기 때문에 예제 데이터로 많이 사용한다.
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/datasets.html
7. Dataset loading utilities
The sklearn.datasets package embeds some small toy datasets as introduced in the Getting Started section. This package also features helpers to fetch larger datasets commonly used by the machine le...
scikit-learn.org
사이킷런이 제공하는 데이터셋 중 머신러닝이 사용하기 좋은 데이터셋
: Toy datasets에는 boston, iris diabetes, digits, innerrud wine, breast cancer 7가지 데이터셋을 제공한다.
Real world datasets에는 olivetti faces, 20 newsgroups, labeled faces, forest covertype, RCV1, Kddcup 99, California housing 등 총 7가지 데이터셋을 제공한다.
예제로 iris diabetes를 사용할 예정
- sepal length
- sepal width
- petal length
- petal width
데이터 준비
사이킷런의 예제 데이터셋은 sklearn 라이브러리의 datasets 패키지 안에 있다.
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
iris = load_iris()
print(dir(iris))
# dir()는 객체가 어떤 변수와 메서드를 가지고 있는지 나열함iris.keys() ===>
dict_keys(['data', 'target', 'frame', 'target_names', 'DESCR', 'feature_names', 'filename', 'data_module'])iris_data = iris.data
print(iris_data.shape)
===> (150, 4)
150개의 데이터가 4개의 정보를 갖고 있음
iris_data[0]
===> array([5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2])
각각 sepal length, sepal width, petal length, petal width를 의미한다.
===> 위의 정보를 가지고 붓꽃의 종류인 setosa, versicolor, virginica 세 가지 중 무엇인지 맞추고 싶음
머신러닝 모델이 출력해야 하는 정답을 라벨 label 혹은 타겟 target이라고 한다.
iris_label = iris.target
print(iris_label.shape)
iris_label(150,)
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2])총 150개의 데이터가 들어가 있다.
target_names: 라벨의 이름을 알 수 있다.
iris.target_names ===> array(['setosa', 'versicolor', 'virginica'], dtype='<U10')
0이면 setosa, 1이면 versicolor, 2면 virginica를 의미한다.
feature_name: 각 features의 설명이 있다.
iris.feature_name ===> ['sepal length(cm)', 'sepal width(cm)', 'petal length(cm)', 'petal width(cm)']
문제지와 정답지 준비
pandas를 사용
붓꽃 데이터셋을 pandas가 제공하는 데이터프레임의 자료형으로 변환
iris_df = pd.DataFrame(data=iris_data, columns=iris.feature_names)label 컬럼 추가
iris_df["label"] = iris.target
iris_df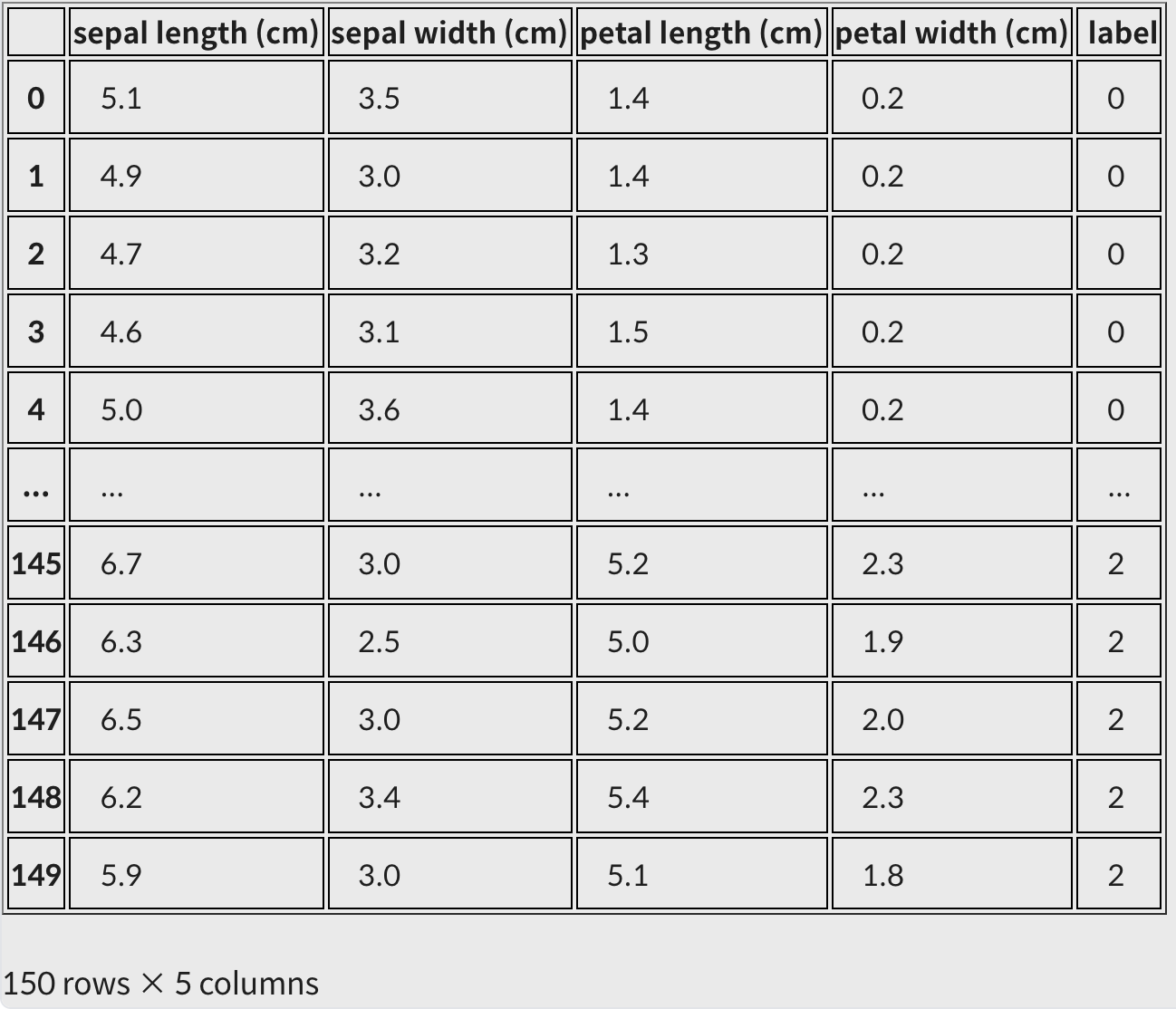
문제지: 머신러닝 모델에게 입력되는 데이터로 feature라고 부르기도 한다. 변수 이름으로는 X를 많이 사용한다.
정답지: 머신러닝 모델이 맞혀야 하는 데이터로 label or target이라고 부르기도 한다. 변수 이름으로는 y를 많이 사용한다.
training dataset 과 test dataset 분류하기
: sklearn.model_selection 패키지의 train_test_split 사용
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris_data,
iris_label,
test_size=0.2,
random_state=7)
print('X_train 개수: ', len(X_train),', X_test 개수: ', len(X_test))train_test_split의 파라미터
1. iris_data: 문제지feature로 4가지의 특징 정보가 있다.
2. iris_lable: 모델이 맞춰야하는 정답값label으로 세 가지 품종이 있다.
===> 학습용 데이터를 생성하며 feature 데이터만 있는 X, 그리고 정답label 데이터만 있는 y를 얻을 수 있다.
===> X데이터셋을 머신러닝 모델에 입력하고 모델이 출력하는 예측 결과를 정답 y와 비교하며 점차 정답을 맞히도록 학습함
3. text_size: test dataset의 크기 조절. 0.2는 전체의 20%를 테스트 데이터로 사용하겠다는 의미
4. random_state: train 데이터와 test 데이터를 분리하는데 적용되는 랜덤성 결정. 컴퓨터에서 랜덤은 특정 로직에 따라 결정되기 때문에 완벽한 랜덤이라고 할 수 없다. 이러한 랜덤을 조절할 수 있는 값이 random_state or random_seed이다. 이 값이 같다면 항상 같은 랜덤 결과를 나타낸다.(다른 사람의 컴퓨터에서도 재현가능하게 하려면 랜덤시드가 필요)===> 120개 train 데이터, 30개 test 데이터로 분류됨
머신러닝 모델 학습시키기
지도학습(Supervised Learning): 정답이 있는 문제에 대해 학습하는 것
비지도학습(Unsupervised Learning): 정답이 없는 문제를 학습하는 것
분류Classification: 입력받은 데이터를 특정 카테고리 중 하나로 분류하는 문제
회귀Regression: 입력받은 데이터에 따라 특정 필드의 수치를 맞히는 문제
의사결정나무 Decision Tree
질문을 던져서 대상을 좁혀나가는 ‘스무고개’ 놀이와 비슷한 개념
https://ratsgo.github.io/machine%20learning/2017/03/26/tree/
의사결정나무(Decision Tree) · ratsgo's blog
이번 포스팅에선 한번에 하나씩의 설명변수를 사용하여 예측 가능한 규칙들의 집합을 생성하는 알고리즘인 의사결정나무(Decision Tree)에 대해 다뤄보도록 하겠습니다. 이번 글은 고려대 강필성
ratsgo.github.io
(엔트로피, 정보량, 지니불순도 등의 정보이론 개념이 포함 ===> 구글링을 통해서 알아보기)
sklearn.tree 패키지 않에 DecisionTreeClassifier 라는 이름으로 내장되어 있다.
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
decision_tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=32)
print(decision_tree._estimator_type)학습하기
decision_tree.fit(X_train, y_train)모델 평가하기
test 데이터로 predict() 예측하기
y_pred = decision_tree.predict(X_test)
y_predarray([2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 0, 2, 0, 2, 2, 2, 0, 0, 1, 2,
1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 1, 2, 2])
예측한 결과에 대한 수치를 정답과 비교하여 확인할 수 있는 방법
scikit-learn에서 sklearn.metrics 패키지 이용
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
accuracy
>>> 0.9정리
# (1) 필요한 모듈 import
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
# (2) 데이터 준비
iris = load_iris()
iris_data = iris.data
iris_label = iris.target
# (3) train, test 데이터 분리
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris_data,
iris_label,
test_size=0.2,
random_state=7)
# (4) 모델 학습 및 예측
decision_tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=32)
decision_tree.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = decision_tree.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))Random Forest
Decision Tree를 여러 개 모아놓은 Random Forest이다. 앙상블Ensemble 기법이라고 한다. 단일 모델을 여러 개 사용하는 방법을 취함으로써 모델 한 개만 사용할 때의 단점을 극복하는 개념
예) 의사결정트리 만들기: 건강 위험도를 예측하기 위해 성별, 키, 몸무게 세 가지 요소보다 더 많은 요소 고려하기. 다른 요소들의 조합으로 두 번째, 세 번째 의사결정트리를 생성한다. 성별, 키, 흡연 여부, 근육량으로 두 번째 트리 만들고, 키, 거주지역, 운동량으로 세 번째 트리를 만든다.
의견 통합: 1,000개의 의사 결정 트리 중 678개의 트리가 건강 위험도가 높다고 의견을 내고, 나머지는 위험도가 낮다는 의견을 냈을 경우 숲은 그 의견들을 통합하여 건강 위험도가 높다고 한다.
===> 의견을 통합하거나 여러가지 결과를 합친은 방식을 앙상블Ensemble method라고 한다.
Random 은 각각의 의사 결정 트리를 만드는데 있어 쓰이는 요소들(흡연 여부, 나이 등)을 무작위적으로 선정한다. 건강 위험도를 30개 요소로 설명할 수 있으면, 의사 결정 트리의 한 단계를 생성하면서 모든 요소들을 고려하지 않는다. 30개 중 무작위로 일부만 선택하여, 그 선택된 일부 중 가장 건강 위험도를 알맞게 예측하는 한 가지 요소가 의사 결정 트리의 한 단계가 된다. (Random Forest의 각각의 의사 결정 트리를 만들기 위해 쓰이는 특성을 랜덤으로 선택한다.)
Random Forest를 완성하는 과정
- 많은 요소를 고려
- Feature가 30개라 했을 때 30개의 Feature를 기반으로 하나의 결정 트리를 만든다면 트리의 가지가 많아질 것이고, 이는 오버피팅 야기
- 30개의 Feature 중 랜덤으로 5개 Feature만 선택해서 하나의 결정 트리 생성
- 반복하여 여러 개의 결정 트리 생성
- 여러 결정 트리들이 내린 예측 값들 중 가장 많이 나온 값을 최종 예측값으로 지정
- 하나의 거대한(깊은) 결정 트리를 만드는 것이 아니라 여러 개의 작은 결정 트리를 만드는 것
- 분류: 여러 개의 작은 결정 트리가 예측한 값들 중 가장 많은 값 / 회귀: 평균
sklearn.ensemble 패키지 내에 존재
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris_data,
iris_label,
test_size=0.2,
random_state=21)
random_forest = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=32)
random_forest.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = random_forest.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))다른 사이킷런 내장 분류 모델
Random Forest
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris_data,
iris_label,
test_size=0.2,
random_state=21)
random_forest = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=32)
random_forest.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = random_forest.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))Support Vector Machine(SVM)
from sklearn import svm
svm_model = svm.SVC()
print(svm_model._estimator_type)
# 코드를 입력하세요
svm_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = svm_model.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))Stochastic Gradient Descent Classifier (SGDClassifier)
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier
sgd_model = SGDClassifier()
print(sgd_model._estimator_type)
# 코드를 입력하세요
sgd_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = sgd_model.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))Logistic Regression
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
logistic_model = LogisticRegression()
print(logistic_model._estimator_type)
# 코드를 입력하세요
logistic_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = logistic_model.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))다양하게 평가해보기
오차행렬

from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)array([[317, 9],
[ 4, 30]])
https://manisha-sirsat.blogspot.com/2019/04/confusion-matrix.html
Confusion Matrix
What is Confusion Matrix and Advanced Classification Metrics? After data preparation and model training, there is model evaluat...
manisha-sirsat.blogspot.com
'AIFFEL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| AIFFEL 아이펠 10일차 (0) | 2022.01.11 |
|---|---|
| AIFFEL 아이펠 사이킷런으로 구현해보는 머신러닝 (0) | 2022.01.10 |
| AIFFEL 아이펠 8일차 (0) | 2022.01.05 |
| AIFFEL 아이펠 다양한 데이터 전처리 기법 (0) | 2022.01.05 |
| AIFFEL 아이펠 7일차 (0) | 2022.01.05 |


